Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, & Viruses Tutorial
Eukaryotes
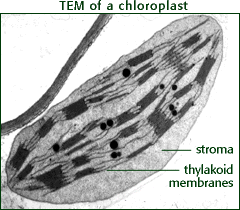
Basic structure
The basic eukaryotic cell contains the following:
|
|
The University of Arizona
Revised: November 8, 1999
Contact the Development Team
http://www.biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 1997-99. All rights reserved.