Childhood Exanthems
by Robin R. Hemphill, MD
- Measles (Rubeola):
Measles is a contagious viral infection characterized by fever, cough,
conjunctivitis, and coryza. There is significant morbidity and mortality associated with this disease.
- Incubation Period: 10-12 days
- Usual Age of Onset: Infants - Young Adults
- Mode of Transmission: Respiratory droplets
- Infective period: from start of prodrome until day 5 of exanthem
- Prodrome: Typical measles: 3 - 4 days of coryza,
conjunctivitis,photophobia, malaise cough, & high fever.
Atypical measles: 2-5 days of high fever, myalgias, & cough.
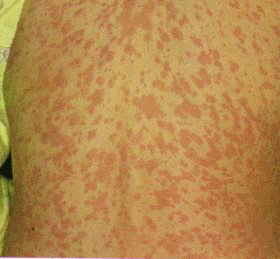
- Exanthem: Typical measles: Erythematous macules & papules starts behind ears & at scalp margin (usually
on the fourth febrile day) then spread to entire body
reaching the feet by the third day. Brown pigmentation during resolution.
Atypical measles: Papular or papulovesicular & often
hemorrhagic. Start on extremities & spread central.
- Enanthem: Koplick spots - appear before exanthem & fade within 2-3 days
of rash. These are small bluish-white papules which appear on the buccal mucosa.
- Complications and Associated Findings:
- Usually, a self-limited disease.
- Otitis media, generalized lymphadenopathy, bronchopneumonia (bacterial or measles), meningitis,
encephalitis, toxic appearance, photophobia may occur.
- Atypical measles: virtually always a lobular or segmental pneumonia.
- Chronic complication: subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
- DDX: Atypical measles, rubella, scarlet fever, roseola, 5th disease, drug eruption, secondary syphilis, mononucleosis.
- Treatment:
- Prevention via prophylactic immunization
- Oral Vitamin A 400,OOOU for severe measles
- Administration of appropriate antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections
- Lab/ Dx: Clinical, acute/conv hemaglutinin inhibition (HAI) serology
- Agent: Paramyxovirus (RNA virus)
Measles Photo
- Scarlet Fever:
Scarlet fever is an infection of the skin and/or tonsils by an
exotoxin-producing strain of group A streptococcus.
- Incubation Period: 1-4 days
- Usual Age of Onset: childhood
- Mode of Transmission: Respiratory droplets or fomites
- Infective period: Contagious early in infection
- Prodrome: 1-3 days of sore throat, fever, myalgias, vomiting, and
abdominal pain.
- Exanthem: Starts 1-3 days after onset of the fever. Begins as a
erythematous (sunburn appearance) rash on
the trunk which has a "sandpaper" feeling when palpated. Perioral pallor
is present. Patia's lines are linear
petechiae which occur in the skin folds. The exanthem fades after 4-5 days
and is followed by desquamation.
- Enanthem: Beefy red pharynx and tonsils. Petechiae on the palate. White to red "strawberry tongue.
- Complications and Associated Findings:
- Nonsuppurative sequelae: rheumatic fever, acute glomerulonephritis
- Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
- DDX: Drug reaction, Staph as cause
- Treatment: Penicillin or Erythromycin
- Lab/ Dx: Throat culture, rising ASO titer
- Agent: Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci
- Rubella:
Rubella is a childhood infection that is manifested by a characteristic
rash. In childhood it usually runs a benign course. However, in pregnant women infection may cause significant congenital abnormalities.
- Incubation Period: 14-21 days
- Usual Age of Onset: adolescents/ young adults
- Mode of Transmission: Respiratory droplets
- Infective period: 7 days before and 5 days after rash
- Prodrome: 1-7 days of malaise, tender post-auricular and occipital adenopathy
- Exanthem: Well defined rose-pink macules and papules which begin on the face and move caudally. Typically the rash resolves within three days. The rash is less confluent than measles.
- Enanthem: Petechiae or reddish macules on the soft palate.
- Complications and Associated Findings:
- There are minimal constitutional symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Arthritis and arthralgias are more common in adults, particularly women.
- Severe fetal complications may occur if infection develop in first half of pregnancy (cataracts, coronary disease, deafness, etc).
- DDX: Other viral exanthems and drug eruptions
- Treatment:
- no specific therapy
- prophylaxis by immunization
- Lab/ Dx: Rubella IgM or acute/convalescent IgG titers
- Agent: Rubella virus
- Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth's Disease):
- Incubation Period: 4-14 days
- Usual Age of Onset: 5-15 days
- Mode of Transmission: Respiratory Droplets
- Infective period: During prodrome and 7 days
after onset of symptoms. Not during rash.
- Prodrome: 1-4 days of mild fever, headache, chills. Patients may be
asymptomatic.
- Exanthem: Bright red "slapped cheeks" followed later by reticulated macules and papules most prominent on the extremities. This rash may wax and wane over the next 7-14 days.
- Enanthem: None
- Complications and Associated Findings:
- Transient arthritis and arthralgias especially in adults.
- Transient aplastic crisis
- Intrauterine infection and fetal death may occur rarely
- DDX: Other viral exanthems
- Treatment: None specific
- Lab/ Dx: Diagnosis is usually clinical, however, IgM assays can be done.
- Agent: Parvovirus B19
- Roseola Infantum(Exanthem Subitum):
- Incubation Period: 7-15 days
- Usual Age of Onset: 6 months-three years
- Mode of Transmission: Unknown
- Infective period: During illness
- Prodrome: High fever for three to five days. Child may appear ill.
- Exanthem: Well defined erythematous blanching macules, distributed on the neck, trunk, and buttocks. Rash
lasts 2-34 hours and typically appears after the fever breaks.
- Enanthem: Erythematous macules and streaks on the soft palate, 48 hours prior to exanthem.
- Complications and Associated Findings:
- Cervical and postauricular adenopathy, mild coryza, cough, headache.
- Complications are rare, but febrile seizures may occur
- DDX: Other exanthems such as enterovirus, adenovirus, rubella, EBV
- Treatment: None specific
- Lab/ Dx: Diagnosis is made clinically
- Agent: Human Herpes Virus
- Chicken Pox (Varicella):
This is a contagious infection that is characterized by pruritic vesicles
which develop into pustules, crusts, and potentially, scars. Infections in adulthood may run a more complicated course.
- Incubation Period: 10-21 days
- Mode of Transmission: Respiratory Droplets,
and uncommonly, direct contact with herpes zoster.
- Usual Age of Onset: 1-14 years
- Infective period: Several days prior to vesicles,
until all lesions are crusted.
- Prodrome: Low grade fever and malaise
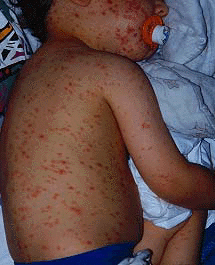
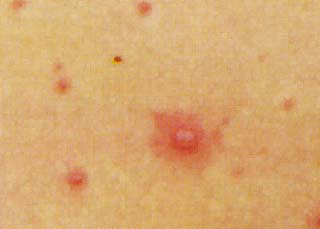
- Exanthem: Macules and papules that become vesicles on an erythematous base ("dew drop on a rose pedal")The rash may start on the face and spreads to the trunk and extremities.
- Enanthem: Ulcers on the palate
- Complications and Associated Findings:
- Course is usually benign in the pediatric population
- Secondary infection of the vesicles
- Varicella pneumonia is common in adult population
- Varicella encephalitis
- Infections in the first-trimester of pregnancy may result in congenital malformations
- DDX: Enteroviruses, generalized herpes infection, bullous form of impetigo
- Treatment:
- Avoid salicylates
- In healthy patient's symptomatic therapy for pruritus is usually adequate
- Treat infected vesicles
- Acyclovir may be considered in early adult infections
- Hospitalization and IV acyclovir for severe varicella, varicella
pneumonitis, varicella infection in
immunocompromised host.
- Varicella-zoster immune globulin may be considered in nonimmune immunocompromised patients
- Lab/ Dx: Usually a clinical diagnosis. Tzank preparation may be done or viral culture
- Agent: Varicella-Zoster Virus
Pox Photo
BACK TO EMERGENCY CENTRAL RESOURCE


