
Carbohydrate Metabolism Regulation Problem Set
Question 4: Insulin Regulation of Glucokinase
Tutorial to help answer the question
Glucokinase is also regulated by insulin in liver, but not via phosphorylation. How is this regulation accomplished?
|
A.
|
Via increased transcription of the gene encoding this enzyme
|
|
B.
|
By recruitment of pre-existing enzyme from the Golgi
|
|
C.
|
Via allosteric regulation by fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase
|
|
D.
|
Activation by association with IRS-1
|
|
E.
|
An inhibitory subunit of the enzyme dissociates after binding cAMP
|
Tutorial
Chronic Insulin Induces Glucokinase
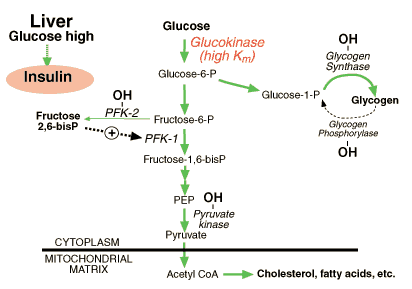
When glucose levels become very high or are chronically high, insulin has another card to play in order to clear glucose from the blood. Recall that glucokinase, a liver enzyme, has a relatively high Kmfor glucose, and therefore only really comes into action when glucose levels are high. This enzyme is well suited for removing glucose from the blood for two reasons.
- First, it is located in liver, a major storage site for excess glucose.
- Second, its high Km will allow it to perform this function without removing too much glucose from the blood (thus depriving other tissues), even if enzyme levels are high.
So, it makes sense that insulin would upregulate this enzyme, and it does so by increasing gene transcription (again, do not worry about the mechanism).
Now, before we move on to consider glucagon action, this is a good time to take a last look at the whole picture of insulin action in liver, which includes coordinated regulation of six enzymes in order to achieve glucose uptake and storage (just follow the green arrows!).
|
![[Problem 4]](problem_4_left.gif) ![[Answer]](answer-2.gif) ![[Problem 5]](problem_5_right.gif)
![[MAINPAGE]](INTRODUCTION.gif) ![[Biochemistry]](biochemistry.gif) ![[Vocabulary]](vocabulary-1.gif) 
The Biology Project
The University of Arizona
March 16, 2000
Contact the Development Team
http://www.biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 2000. All rights reserved.
|

